Testing and Quality Control Processes for FastTurn PCB
Introduction
In the modern electronics industry, producing reliable printed circuit boards (PCBs) is crucial for delivering high-performance devices. A FastTurn PCB is not just about speed; it’s also about precision, durability, and reliability. Companies rely on strict testing and quality control processes to ensure every board meets rigorous standards before it reaches the customer. These processes help prevent defects, reduce costs, and maintain customer trust.
With the increasing demand for rapid PCB production, it becomes even more important to maintain quality while meeting tight deadlines. FastTurn PCB services combine speed with advanced testing methods, allowing engineers and designers to accelerate product development without compromising on performance. By understanding these processes, businesses can better appreciate the value of a high-quality FastTurn PCB.
Visual Inspection and Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Visual inspection remains one of the first steps in quality control for a FastTurn PCB. Trained technicians examine each board for obvious defects such as misaligned components, soldering issues, or broken traces. Even minor visual flaws can lead to performance problems, making this initial check critical. Visual inspection ensures that defective boards are identified before moving to more complex testing stages, saving both time and money.
Complementing manual checks, Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) uses high-resolution cameras and software to detect surface defects with greater accuracy. AOI systems can identify missing components, incorrect placements, or solder bridging that human eyes might miss. This combination of visual inspection and AOI ensures that every FastTurn PCB leaving the production line meets precise specifications and reduces the likelihood of failures during assembly or operation.
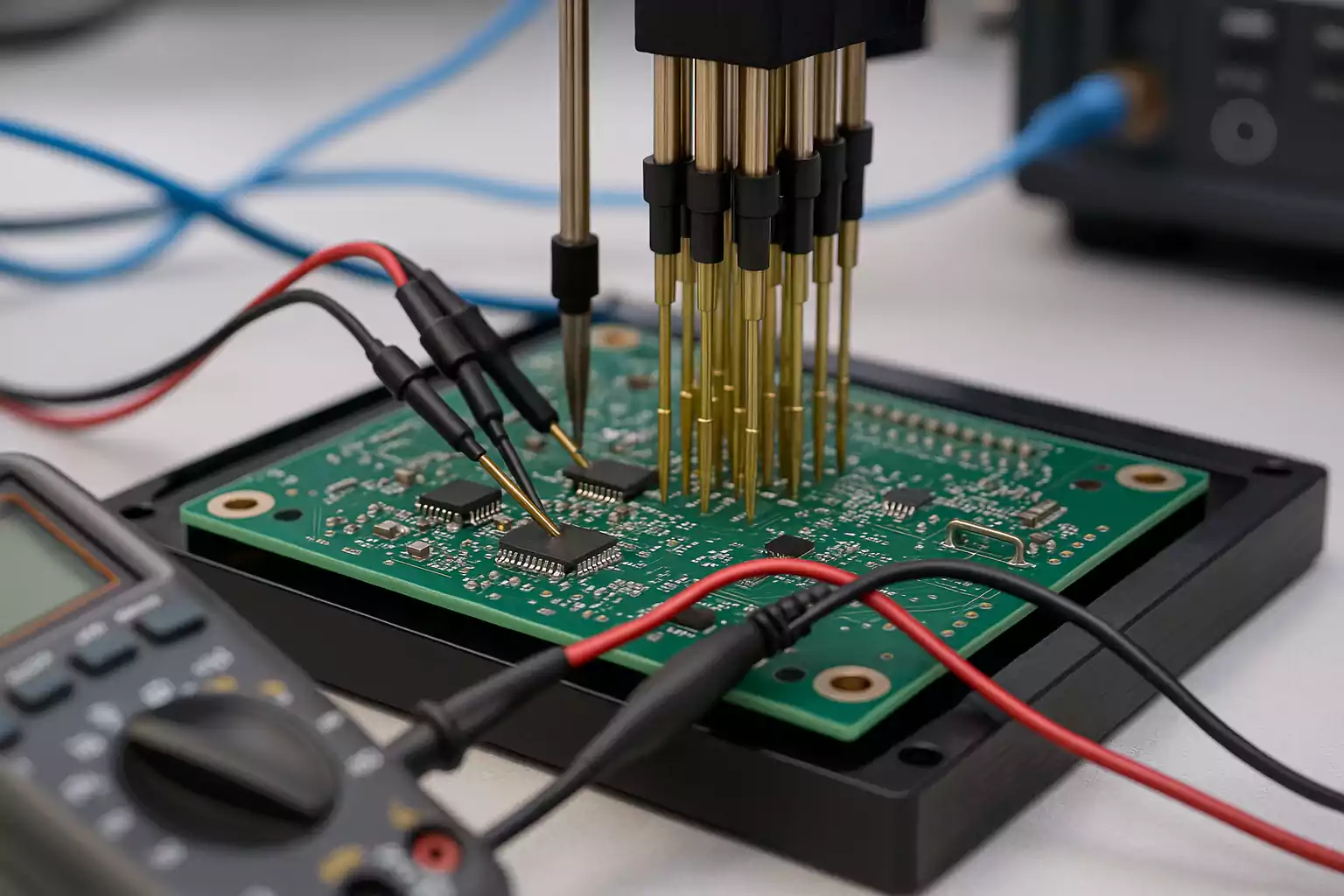
Electrical Testing Methods
Electrical testing is another vital component of FastTurn PCB quality control. These tests verify that the circuits function correctly and that all electrical connections meet design requirements. One common approach is the in-circuit test (ICT), which checks for shorts, opens, and component integrity. ICT helps identify hidden problems that could affect the board’s performance once installed in a device.
Functional testing is also essential. This process simulates real-world operating conditions to ensure the board performs as expected under load. By running functional tests, manufacturers can confirm that the FastTurn PCB will operate reliably in its intended environment. Combining ICT and functional testing provides a robust framework for detecting both minor and critical defects, ensuring the final product is safe and reliable for customers.
Soldering Quality and Component Placement
Soldering quality is a major factor in the performance and lifespan of a FastTurn PCB. Poor solder joints can cause intermittent connections, overheating, or complete board failure. Quality control teams carefully monitor the soldering process using X-ray inspection or automated optical systems. These techniques allow manufacturers to detect insufficient solder, voids, or misaligned components before boards leave the factory.
Proper component placement is equally important. Even small misalignments can affect signal integrity, cause shorts, or prevent boards from fitting into assemblies correctly. FastTurn PCB services emphasize precise placement using advanced pick-and-place machines, combined with post-placement inspections. This meticulous approach ensures that every component is securely and accurately mounted, contributing to the board’s overall reliability.
Environmental and Stress Testing
Environmental testing is essential for ensuring a FastTurn PCB can withstand the conditions it will encounter during its lifetime. Boards may be exposed to heat, humidity, vibration, or temperature cycling, all of which can affect performance. Environmental stress tests simulate these conditions to evaluate the board’s durability. Boards that fail these tests are corrected or rejected, preventing potential failures in the field.
Thermal cycling tests, for example, repeatedly heat and cool the PCB to detect weaknesses in solder joints or component adhesion. Vibration testing simulates transportation or operational stress to ensure the board can endure mechanical shocks. These stress tests help manufacturers deliver FastTurn PCBs that remain reliable even in demanding applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems.
Statistical Process Control and Continuous Improvement
Maintaining consistent quality in FastTurn PCB production requires more than one-off inspections. Statistical Process Control (SPC) uses data collected throughout the manufacturing process to monitor trends and detect variations before they become defects. By analyzing metrics such as defect rates, solder quality, and placement accuracy, manufacturers can take proactive steps to improve processes and reduce errors.
Continuous improvement programs complement SPC by implementing lessons learned from previous production runs. This approach ensures that each batch of FastTurn PCB is better than the last, fostering efficiency and reliability. By integrating statistical analysis with ongoing process refinement, manufacturers create a culture of quality that benefits both the production team and the end customer.
Documentation and Compliance Standards
Comprehensive documentation is a key part of quality control for FastTurn PCB services. Each board undergoes meticulous record-keeping, including inspection reports, test results, and assembly notes. Proper documentation allows manufacturers to trace defects, verify compliance with design specifications, and provide customers with transparency regarding product quality.
Compliance with industry standards, such as IPC standards for PCB manufacturing, is also critical. These standards ensure that FastTurn PCBs meet established safety, reliability, and performance benchmarks. Adhering to recognized guidelines not only enhances product quality but also strengthens customer confidence, making FastTurn PCB an attractive option for engineers and companies seeking dependable and rapid PCB solutions.
Conclusion
Testing and quality control are the backbone of reliable FastTurn PCB manufacturing. From visual inspections and AOI to electrical testing, environmental stress checks, and statistical process control, every step ensures the final product meets high-performance standards. High-quality soldering, precise component placement, and adherence to industry standards further guarantee the board’s reliability and longevity.
By investing in rigorous quality control processes, FastTurn PCB manufacturers provide products that combine speed with accuracy, allowing engineers to accelerate their projects without sacrificing performance. These practices not only reduce the risk of failures but also build trust with customers, making FastTurn PCB an essential partner in today’s fast-paced electronics industry.




